Maurizio Polemio (a), Manuel Sapiano (b), Francesca Santaloia (a), Alessia Basso (a), Vittoria Dragone (a), Giorgio De Giorgio (a), Pierpaolo Limoni (a), Livia Emanuela Zuffianò (a), Mangion John (b) & Micheael Schembri
(a) Istituto di Ricerca per la Protezione Idrogeologica – CNR, Bari, Italy.
(b) Energy and Water Agency – EWA, Luqa, Malta.
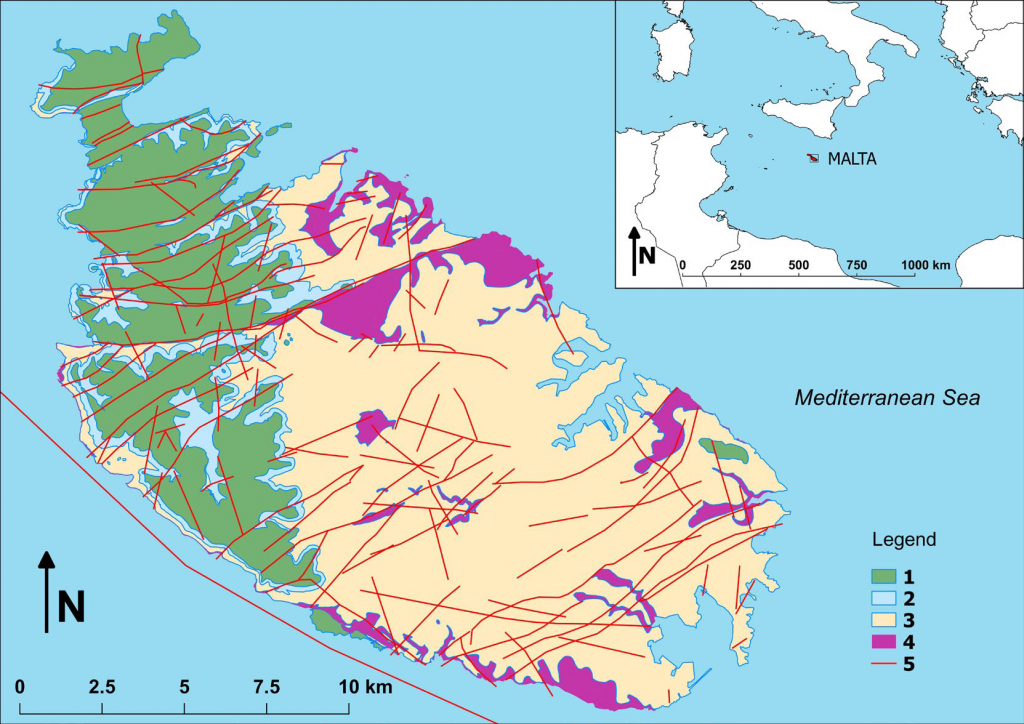
The Maltese Islands are located in the central Mediterranean area,
on the Malta-Sicily Platform. The archipelago consists of three main
islands, Malta, Gozo and Comino, and several other small uninhabited
islets. Malta, the largest of the three islands, has an extent of 246 km2.
The aim of this paper is to describe the collaboration between CNRIRPI
and EWA (Energy and Water Agency of Malta) and the efforts to
upgrade the hydrogeological knowledge of the Malta Island, pursuing
the sustainable utilisation of groundwater resources. This will support
the water management activities for optimizing the use of Malta’s
groundwater resources. Firstly, a review of the hydrogeological
environment of the aquifer systems has been undertaken, identifying
so some important data gaps that should be filled up. The eventual
groundwater body management tool to be developed under this
collaborative initiative will enable the formulation and testing of
updated groundwater exploitation strategies. These plans ensure the
protection of the groundwater bodies from regional and localized
sea-water intrusion, whilst taking full consideration of the potential
effects of climate change, including the variability of recharge, sea
level and seawater salinity.
The complete article is avaible on:
Rend. Online Soc. Geol. It., Vol. 47 (2019), pp. 85-89, https://doi.org/10.3301/ROL.2019.16